variadic templates
1.可变参数函数实现原理
指定参数的函数实现,通过指定的参数名访问
不指定参数的函数实现,函数调用的参数进行压栈处理(从右到左进行压栈)
可变参数函数:参数个数可变、参数类型不定的函数
“…” 表示0个或多个类型未知的参数
最常见的例子:
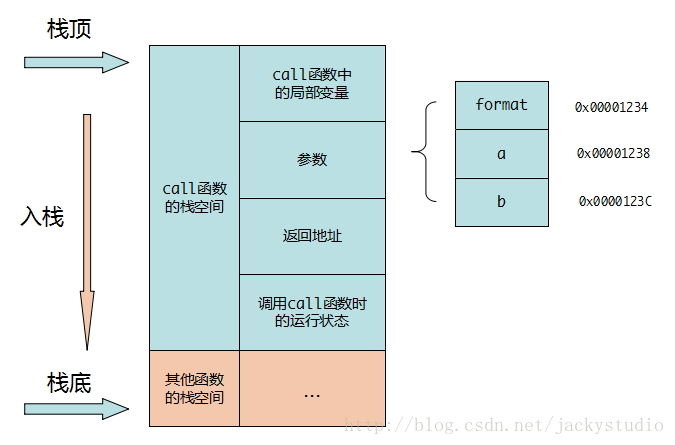
int printf(const char * format, ...)
调用:
int a=5;
char b='b';
printf("%d and %c",a,b);
参数压栈顺序:b,a,format
函数调用内存结构:
2.声明和定义
对不定参数部分用”…“表示
可变参数至少包含一个参数,用来寻址,实现对所有参数的访问
已知的指定参数必须声明在函数最左端
错误的声明:
void func(...)
或者
void func(..., int a);
3.示例
求和。第一个参数指定要计算的值的个数
格式化字符串。第一个参数指定占位符
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdarg>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int sum(int num,...) //利用变长函数进行求和运算
{
int sumval=0;
va_list args; //定义一个可变参数列表
va_start(args,num); //初始化args指向强制参数arg的下一个参数
while(num--)
{
sumval+=va_arg(args,int); //获取参数的值
}
va_end(args); //释放args
return sumval;
}
string format(const char* format, ...) //格式化字符串
{
string var_str;
va_list ap;
va_start(ap, format);
int len = _vscprintf(format, ap);
if (len > 0)
{
vector<char> buf(len + 1);
vsprintf(&buf.front(), format, ap);
var_str.assign(buf.begin(), buf.end() - 1);
}
va_end(ap);
return var_str;
}
int main()
{
cout<<sum(5,10,23,78,65,9)<<endl;
cout<<sum(8,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8)<<endl;
cout<<format("%s#%s#%s","this","is","me");
//cout<<sum(5,10.23,23.78,78.59,65.12,9.08)<<endl;
return 0;
}
参数类型不匹配,程序会出错,可能导致程序崩溃。
4.可变参数模板
“…” 表示0个或多个类型未知的参数,于是可以帮助我们完成递归
#include <iostream>
#include <bitset>
using namespace std;
void print()
{
}
template <typename T,typename... Types> //...用于模板参数
void print(const T& firstArg, const Types&... args)//...用于函数参数类型
{
cout<<firstArg<<endl;
print(args...);//...用于函数参数
}
int main()
{
print(7.5, "hello", bitset<16>(377),42);
return 0;
}
运行结果:

template<typename... Types>
void print(const Types&... args)
{
}
5.调用关系
案例1:
class CustomerHash{
public:
std::size_t operator()(const Customer& c) const{
return hash_val(c.fname,c.lname,c.no);
}
};
template<typename...Types>
inline size_t hash_val(const Types&... args) //函数1
{
size_t seed=0;
hash_val(seed,args...);
return seed;
}
template<typename T, typename... Types>
inline void hash_val(size_t& seed, const T& val, const Types&... args) //函数2
{
hash_combine(seed,val);
hash_val(seed,args...);
}
template <typename T>
inline void hash_val(size_t& seed, const T& val) //函数3
{
hash_combine(seed,val);
}
template <typename T>
inline void hash_combine(size_t& seed, const T&val) //函数4
{
seed^=std::hash<T>()(val)+0x9e3779b9+(seed<<6)+(seed>>2);
}
案例2:
template<typename... Values> class tuple;
template<>class tuple<>{};
template<typename Head,typename... Tail>
class tuple<Head,Tail...>:private tuple<Tail...>
{
typedef tuple<Tail...> inherited;
public:
tuple(){}
tuple(Head v,Tail... vtail):m_head(v),inherited(vtail...){}
typename Head::type head(){return m_head;}
inherited& tail(){return *this;}
protected:
Head m_head;
};
tuple<int,float,string> t(41,6.3,"nico");
t.head() //41
t.tail() //6.3, nico
t.tail().head() //6.3
&(t.tail) //nico
6.小结
…就是一个所谓的包(pack)
用于template parameters,就是template parameters pack (模板参数包)
用于function parameter types,就是function parameter types pack(函数参数类型包)
用于function parameters,就是function parameters pack(函数参数包)